Effect of trampling and digging from shellfishing on Zostera noltei (Zosteraceae) intertidal seagrass beds
Abstract
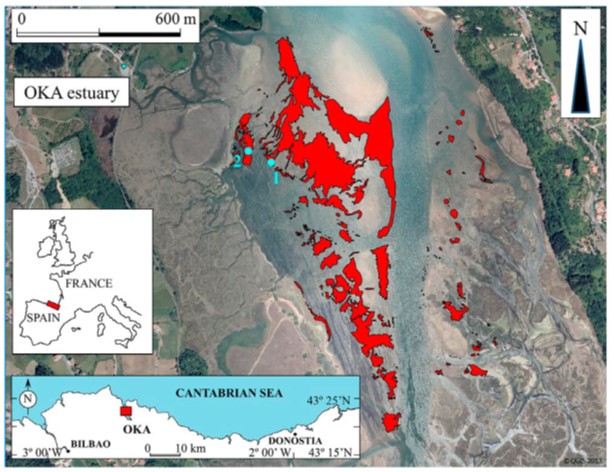
Seagrass beds are among the most valuable ecosystems in the world but they are also among the ones most affected by human activities, and they have decreased significantly in recent decades. In many areas, such as in the Basque Country (northern Spain), seagrass beds occupy areas that are also of interest for human activities such as recreation and shellfishing. They may therefore face a number of pressures that cause damage or irreversible states. Taking into account the limited distribution of seagrass beds in the Basque Country and the interest in their conservation, an eight-month field experiment focusing on the Zostera noltei growing season was carried out to evaluate the effect of shellfish gathering. We used generalized linear models to assess different intensities of trampling and digging, as the most important pressures of shellfishing applied to Zostera noltei beds. The results indicated that shoot density of Z. noltei was negatively altered by trampling treatments and positively affected (as a recovery) by digging treatments. This finding suggests that shellfishing adversely affects seagrass abundance and is potentially responsible for its low density in the Oka estuary. Our findings are important for management and should be taken into account in seagrass conservation and restoration programmes.