Climate change impacts on coastal and pelagic environments in the southeastern Bay of Biscay
Abstract
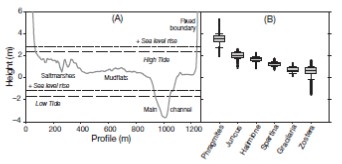
The impacts of global climate change on the Basque coast and the pelagic systems within the southeastern Bay of Biscay are reviewed. Climate projections under greenhouse gas emission scenarios indicate that this area will experience changes in climate throughout the 21st century, including warming of surface air (especially heat wave episodes), intensification of extreme daily rainfall (10%), warming of the upper 100 m of the ocean layer (1.5 to 2.05°C), and sea level rise (SLR; 29 to 49 cm). Observations made in the bay throughout the 20th century for air temperature and mean sea level are in agreement with these projections. Trends in ocean-climatic historical observations within the area, including sea temperature, precipitation, upwelling/downwelling, turbulence and wave climate, are also reviewed. The main impacts on the coast are expected to be from SLR, especially in low-lying areas (mostly urbanised) within estuaries. Sandy beaches are also expected to undergo significant mean shoreline retreats of between 25 and 40% of their width. As the sea level rises, the natural migration of saltmarshes and intertidal seagrasses landward will be constrained, in most cases, by existing anthropogenic fixed boundaries. Empirical relationships between the distribution and dynamics of the long-term biological measures (plankton, primary production, benthos, and fisheries) on the one hand, and ocean-climatic variability on the other, indicate that pelagic and coastal water ecosystems will be affected by ocean warming, increased stratification, shifts in anomaly patterns and streamflow regimes. The largest uncertainties are associated with the lack of down-scaled projections within the bay on ocean circulation, ocean-meteorological indices, wave climate and ocean acidification.